Components
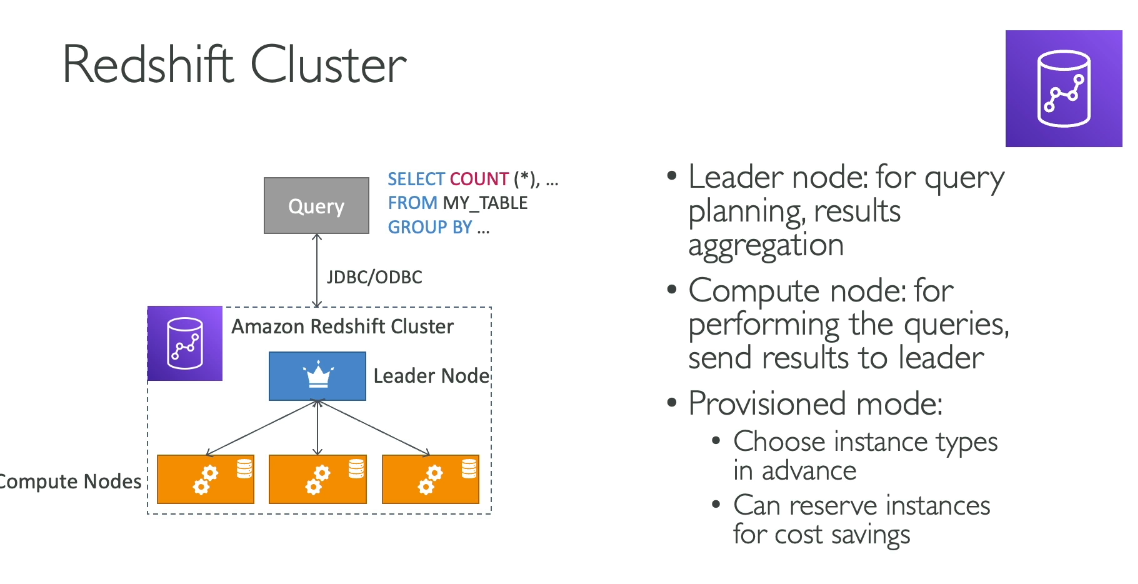
1. Leader Node
- Role: Manages the entire cluster.
- Responsibilities:
- Receives queries from clients (BI tools, SQL clients, etc.).
- Parses, optimizes, and generates query execution plans.
- Distributes the execution tasks to the compute nodes.
- Aggregates results from compute nodes and returns the final result to the client.
- No Data Storage: The leader node does not store any data; it only coordinates.
2. Compute Nodes
- Role: Store and process the actual data.
- Responsibilities:
- Execute query fragments assigned by the leader node.
- Perform computations in parallel across multiple nodes and slices.
- Return intermediate results to the leader node.
- Storage: Data is stored in columnar format for efficient compression and retrieval.
- Scalability: The number and type of compute nodes determine the cluster’s processing power and storage capacity.
3. Node Slices
- Role: Subdivision of compute nodes to parallelize data processing.
- Details:
- Each compute node is divided into slices, and each slice gets a portion of the node’s memory, CPU, and disk.
- Data is distributed across slices for even processing.
4. Cluster
- A Redshift cluster is a collection of one leader node and one or more compute nodes.
- Nodes can be scaled up or down to meet workload requirements.
- Clusters can be resized to add more nodes or migrate to different node types.
5. Network Layer
- Nodes communicate using high-speed, secure connections within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
- Redshift integrates with AWS services like S3 and Glue for data loading and transformation.

Data Distribution and Processing
Data Distribution:
Data is distributed across compute nodes and slices based on the distribution style:
- EVEN: Data is spread evenly across all slices.
- KEY: Data is distributed based on the value of a specified column (used to colocate related data).
- ALL: A full copy of the data is stored on every node (useful for small lookup tables).
Massively Parallel Processing (MPP):
Queries are split into smaller tasks and distributed to compute nodes.
Each node processes its portion of the data in parallel, improving query performance.
Columnar Storage:
Data is stored column-by-column instead of row-by-row.
Reduces the amount of data read during queries, which speeds up analytics workloads.
Scalability and Storage
Scalability:
Add or remove compute nodes based on workload.
Use RA3 nodes to separate compute and storage, allowing independent scaling.
Storage:
RA3 nodes offer managed storage, automatically offloading cold data to Amazon S3 while keeping frequently accessed data on faster local storage.
High Availability and Fault Tolerance
Replication:
Data is automatically replicated within the cluster and to Amazon S3 for backup.
Automatic Recovery:
If a node fails, Redshift automatically re-replicates data and replaces the node.
Security
Encryption:
Data is encrypted at rest (using AWS Key Management Service or customer-managed keys) and in transit (using SSL).
Access Control:
Integrates with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for fine-grained access control.
Supports VPC for network isolation.
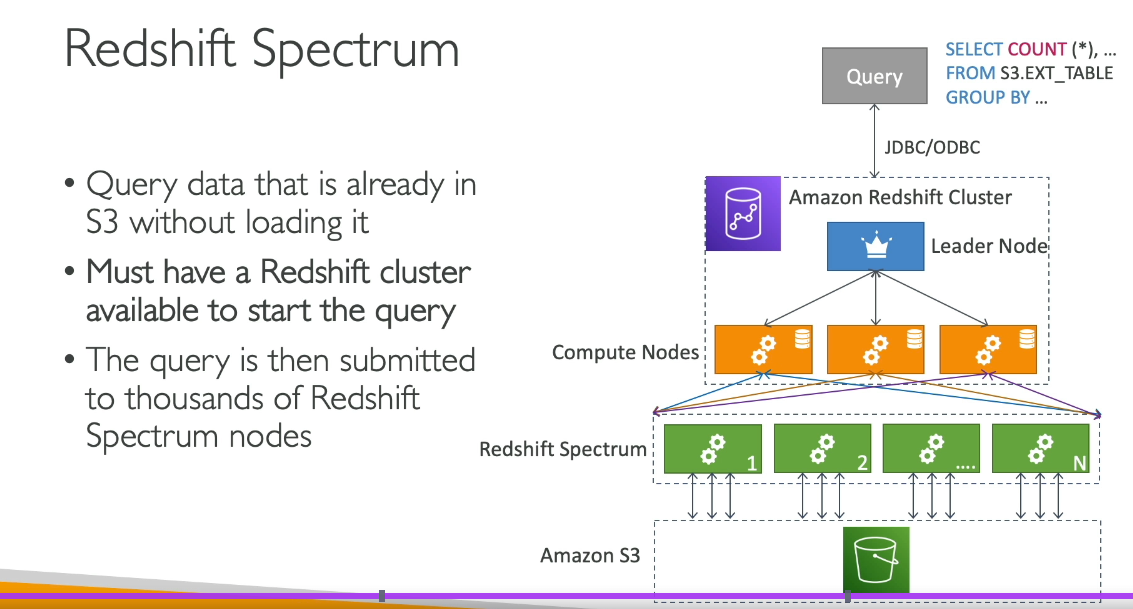
Amazon Redshift Spectrum
Purpose: Extends Redshift’s architecture to query data directly in S3.
How It Works:
Uses the Redshift cluster for processing and leverages a fleet of Spectrum workers to scan and process S3 data in parallel.
Enables a “data lake” architecture by combining structured data in Redshift with semi-structured/unstructured data in S3.