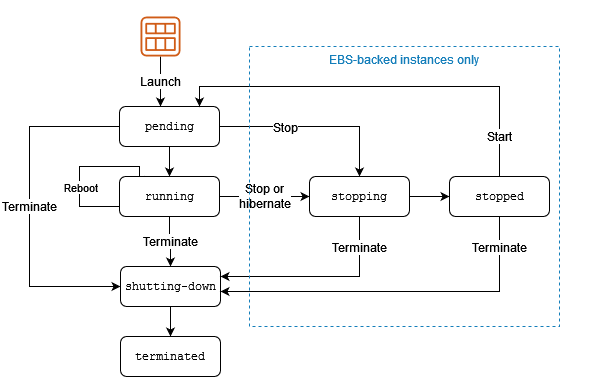
Only an EBS-backed instance can be stopped and started, instance store-backed instance cannot be stopped and started.
Rebooting an instance is equivalent to rebooting an operating system. The instance remains on the same host computer and maintains its public DNS name, private IP address, and any data on its instance store volumes. It typically takes a few minutes for the reboot to complete, but the time it takes to reboot depends on the instance configuration.
Rebooting an instance doesn’t start a new instance billing period; per second billing continues without a further one-minute minimum charge.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ec2-instance-lifecycle.html
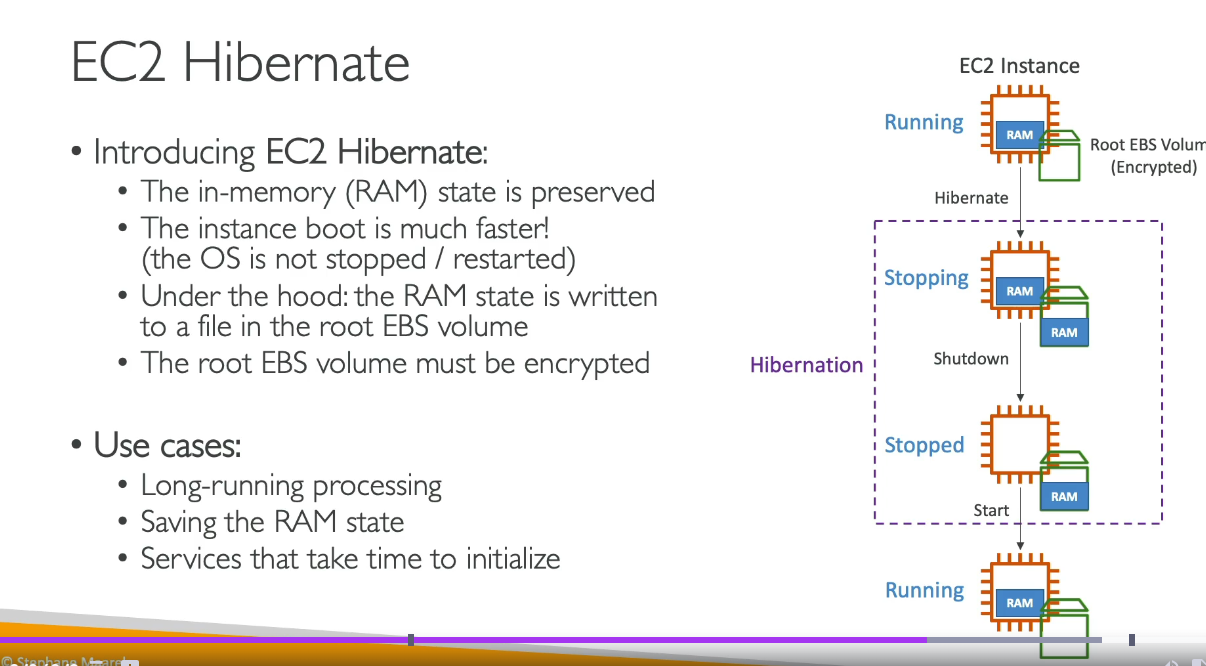
Hibernating
When you hibernate an instance, Amazon EC2 signals the operating system to perform hibernation (suspend-to-disk). Hibernation saves the contents from the instance memory (RAM) to your Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) root volume. Amazon EC2 persists the instance’s EBS root volume and any attached EBS data volumes. When your instance is started:
- The EBS root volume is restored to its previous state
- The RAM contents are reloaded
- The processes that were previously running on the instance are resumed
- Previously attached data volumes are reattached and the instance retains its instance ID
You can hibernate an instance only if it’s enabled for hibernation and it meets the hibernation prerequisites.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/Hibernate.html