On Demand delivery of IT resources, particularly: compute power, application hosting, database applications, networking and more.
Cloud computing models: On Premises, Hybrid, Cloud.
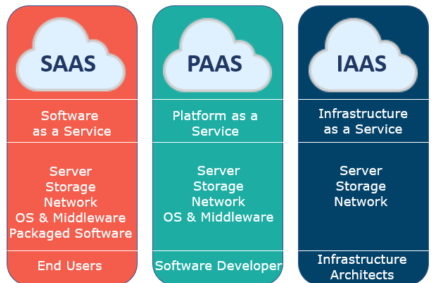
Types of cloud computing:
IaaS – Infrastructure as a service: network, compute, data storage.
PaaS – Doesn’t require managing underlying structure focus on development and manage your applications.
SaaS – complete product that is run and managed by the service provider.
Characteristics of the Cloud:
- On demand self service
- Broad network access
- Multi-tenancy and resource pooling
- Rapid elasticity and scalability
- Measured service
Problems solved by the Cloud:
Flexibility – change resource type when needed.
Cost-effectiveness – pay as you go, for what you use.
Scalability – accommodate larger loads by increasing hardware characteristics as adding more resources.
Elasticity – ability to scale out/in when needed.
High Availability and fault tolerant – built across data centers.
Agility – rapid development, test and launch of software applications.
Benefits of the Cloud:
- Trade Upfront expenses for Variable expenses (CAPEX -> OPEX).
- Stop focusing on data centers, focus on customers.
- Stop guessing capacity.
- Benefit from massive economies of scale. Benefits from customers aggregate usage with price drops per unit used.
- Increase provision speed and business agility.
- Go global in minutes.
Economic model of AWS:
Free Tier – some services are always free, some 12 month free.
On-demand – full pricing play-as-you-go but no contract.
Reservations – contracts for 1/3 years.
Volume discounts – pay less per units as you use more.
Price drops – random price cuts done by AWS.
Cloud native design for AWS:
Design for failure
avoid single points of failure -> resiliency and auto-recovery
Decouple components
tight coupling – > loosely coupled, put a queue or scaling layer between components
Implement elasticity
Think parallel
increase concurrency -> do things in parallel