Benefits of the cloud
Trade upfront expenses vs variables expenses (CAPEX -> OPEX)
Stop focus on datacenters (offload)
Scalability vs guess capacity (stop guessing capacity)
Benefits from massive economy of scale
Global deployment options

Cloud economics

Cloud native design
Design for failure → Resiliency and auto-recovery
Decouple components → Tight coupling to loosely coupled
Implement elasticity → Large expansion and contracting
Think parallel → Increase concurrency
Cloud models
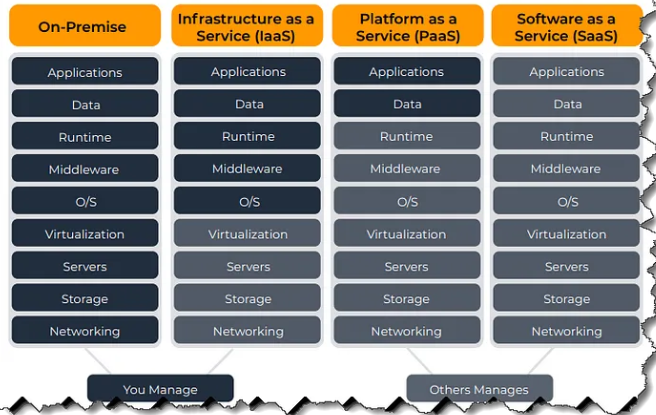
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
Cloud infrastructure services, compute and storage resources.
ex: EC2, EBS, EFS
PaaS – Platform as a Service
Cloud computing service, service that supplies an environment to enable users to develop, run, and manage data without the complexity of managing the infrastructure.
ex: Beanstalk, RDS, Lambda
Saas – Software as a Service
Cloud applications service.
ex: payroll appl, HR solutions
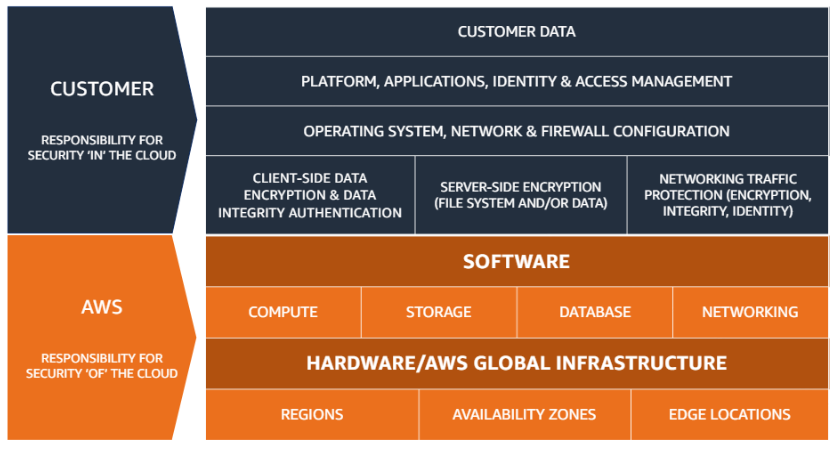
Shared responsibility model
Compliance
Organizations in specific industries must adhere to certain rules and guidelines specific
to that industry (Finance, Health, Federal Government).
Compliance and regulatory frameworks are sets of guidelines and best practices.
Organizations follow these guidelines to meet regulatory requirements, improve
processes, strengthen security, and achieve other business goals.
- Healthcare industry – HIPAA/HITECH
- Payment card industry – PCI DSS
Compliance is a shared responsibility between customers and AWS.
AWS undergoes certifications, reviews, and audits by various governing bodies.
These audit reports are made available to customers using AWS Artifact. Artifact allows
customers to review and accept agreements to maintain compliance.