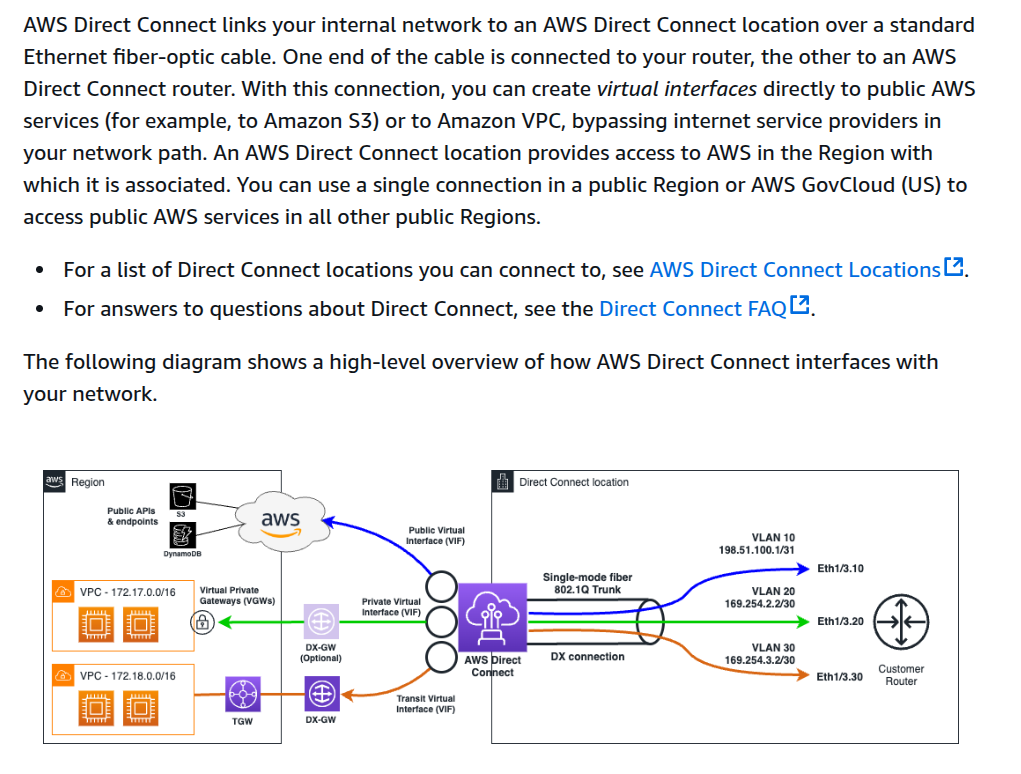

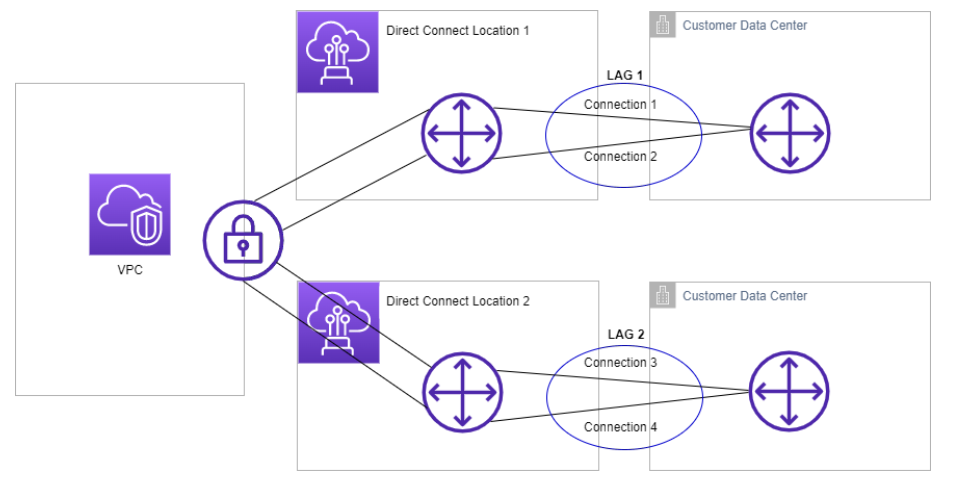
You can use multiple connections to increase available bandwidth. A link aggregation group (LAG) is a logical interface that uses the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) to aggregate multiple connections at a single AWS Direct Connect endpoint, allowing you to treat them as a single, managed connection. LAGs streamline configuration because the LAG configuration applies to all connections in the group.
DX Gateway vs Transit Gateway
Purpose
- Direct Connect Gateway (DX Gateway):
Enables you to connect your on-premises network to one or more VPCs across different AWS regions using AWS Direct Connect. It’s ideal for private, dedicated connections to AWS. - Transit Gateway (TGW):
Acts as a central hub to connect VPCs, VPNs, and Direct Connect within a region. It simplifies large-scale network architectures by consolidating routing.
Connectivity
- DX Gateway:
Provides connectivity from on-premises to multiple VPCs. Does not allow VPC-to-VPC communication directly. - TGW:
Allows interconnection between multiple VPCs, VPNs, and Direct Connect. Supports inter-region peering with other TGWs.
Use Case
- DX Gateway:
Best when you need to connect your data center to AWS over Direct Connect and reach multiple VPCs in different regions. - TGW:
Best when you need centralized routing between multiple VPCs and other networks within or across regions.
Routing
- DX Gateway:
Uses Virtual Private Gateways (VGWs) for each VPC. Routes are more static and controlled per VIF (virtual interface). - TGW:
Uses its own route tables, supports dynamic routing (BGP), and allows granular control of traffic between attachments.
Regional Scope
- DX Gateway:
Global. Can connect to VPCs in any AWS region (excluding China). - TGW:
Regional by default. Supports inter-region connectivity through TGW peering, but this is not transitive.
Security and Control
- DX Gateway:
Simple, but limited control over intra-AWS traffic and visibility. - TGW:
More advanced controls, with support for traffic filtering, monitoring, and firewall integration.